Sleep is a fundamental necessity of life, as important as food and water. It allows the body to rest, repair tissues, consolidate memories, and regulate essential bodily functions. However, millions of people around the world struggle with sleep disorders that disrupt their ability to get a restful night’s sleep. These disorders can significantly impact both physical and mental health, leading to daytime fatigue, cognitive impairment, emotional instability, weakened immunity, and an increased risk of chronic conditions like heart disease, diabetes, and obesity.
Understanding sleep disorders is crucial because they often go undiagnosed, with individuals dismissing their symptoms as mere bad sleep habits. In this article, we will explore the five most common types of sleep disorders: insomnia, sleep apnea, restless legs syndrome (RLS), narcolepsy, and parasomnias. We will break down what each disorder entails, discuss its causes and symptoms, and explore the treatment options available. By the end, you’ll have a clear understanding of these conditions and the steps you can take to improve sleep quality and overall health.
1. Insomnia: The Most Common Sleep Disorder
What Is Insomnia?
Insomnia is a sleep disorder characterized by persistent difficulty falling asleep, staying asleep, or waking up too early and being unable to go back to sleep. It is one of the most widespread sleep disorders, affecting millions worldwide. The condition can be classified into two types:
- Acute Insomnia: Short-term insomnia that lasts for a few days or weeks, often triggered by stress or sudden life changes.
- Chronic Insomnia: A long-term condition where sleep disturbances occur at least three times per week for three months or longer.
Causes of Insomnia
There are several factors that contribute to insomnia, including:
- Stress and Anxiety: Daily worries, workplace pressure, financial concerns, or relationship issues can keep the mind overly active at night, making relaxation difficult.
- Poor Sleep Hygiene: Irregular sleep schedules, excessive screen exposure before bed (such as using smartphones and laptops), consuming stimulants like caffeine and nicotine late in the day, and an uncomfortable sleep environment can interfere with normal sleep patterns.
- Medical Conditions: Chronic pain conditions like arthritis, asthma, heart disease, and acid reflux can cause discomfort that makes it difficult to sleep well.
- Medications: Certain prescription drugs, such as antidepressants, stimulants, and blood pressure medications, may interfere with the body’s ability to fall asleep naturally.
Symptoms of Insomnia
The primary signs of insomnia include:
- Difficulty falling asleep even when tired.
- Frequently waking up throughout the night and struggling to go back to sleep.
- Waking up much earlier than desired and feeling unrested.
- Daytime fatigue, grogginess, irritability, and difficulty concentrating.
- An increased reliance on sleep aids, alcohol, or caffeine to manage sleep problems.
Treatment for Insomnia
To address insomnia effectively, a combination of lifestyle changes and medical interventions may be necessary:
- Lifestyle Adjustments: Establishing a fixed bedtime and wake-up schedule, avoiding screens before bed, creating a relaxing pre-sleep routine, and making the bedroom conducive to sleep (cool, dark, and quiet) can improve sleep quality.
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy for Insomnia (CBT-I): This is an evidence-based psychological therapy that helps individuals identify and change negative thought patterns and behaviors that contribute to sleeplessness.
- Medication: In cases where lifestyle adjustments do not suffice, doctors may prescribe sleep aids, but these should only be used under strict supervision and for short durations to avoid dependency.
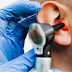
2. Sleep Apnea: Interrupted Breathing During Sleep
What Is Sleep Apnea?
Sleep apnea is a potentially serious sleep disorder in which breathing repeatedly stops and starts during sleep, leading to disrupted rest and reduced oxygen supply to the brain and body. There are two main types:
- Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA): The most common type, caused by the relaxation of throat muscles, which leads to airway blockage.
- Central Sleep Apnea (CSA): A less common condition where the brain fails to send the correct signals to the muscles that control breathing.
Causes of Sleep Apnea
- Obesity: Excess weight, especially around the neck, can cause airway obstruction, increasing the risk of OSA.
- Smoking and Alcohol Consumption: These substances relax the throat muscles, making airway collapse more likely.
- Genetic and Aging Factors: Family history and aging contribute to a higher risk of developing sleep apnea.
Symptoms of Sleep Apnea
- Loud snoring and choking or gasping for air during sleep.
- Frequent awakenings at night, sometimes without recollection.
- Morning headaches, dry mouth, and sore throat upon waking.
- Extreme daytime drowsiness and difficulty concentrating.
Treatment for Sleep Apnea
- Lifestyle Changes: Weight loss, quitting smoking, reducing alcohol consumption, and sleeping on one’s side can alleviate mild cases.
- CPAP (Continuous Positive Airway Pressure) Therapy: A machine that delivers air pressure through a mask to keep the airways open during sleep.
- Surgery: In severe cases, surgical interventions may be necessary to remove obstructions.
3. Restless Legs Syndrome (RLS): Uncontrollable Leg Movements
What Is RLS?
Restless Legs Syndrome (RLS) is a neurological condition characterized by an uncontrollable urge to move the legs due to discomfort, especially in the evening or nighttime.
Causes of RLS
- Genetics: The condition often runs in families.
- Iron Deficiency: Low iron levels can contribute to symptoms.
- Underlying Conditions: Kidney disease, diabetes, and Parkinson’s disease increase the risk.
Symptoms of RLS
- Tingling, itching, or crawling sensations in the legs.
- Symptoms worsen when resting and improve with movement.
Treatment for RLS
- Lifestyle Changes: Regular exercise, stretching, and avoiding caffeine/alcohol before bed.
- Iron Supplements: If an iron deficiency is present.
- Medications: Dopamine agonists may be prescribed in severe cases.
4. Narcolepsy: Excessive Daytime Sleepiness
What Is Narcolepsy?
Narcolepsy is a chronic disorder that causes excessive daytime drowsiness and sudden sleep attacks.
Causes of Narcolepsy
- Deficiency in Hypocretin: A brain chemical that regulates wakefulness.
- Autoimmune and Genetic Factors: Some cases result from immune system dysfunction.
Symptoms of Narcolepsy
- Uncontrollable sleep attacks.
- Sudden muscle weakness (cataplexy).
- Sleep paralysis.
Treatment for Narcolepsy
- Medication: Stimulants like Modafinil to promote wakefulness.
- Scheduled Naps: Short naps help manage drowsiness.
5. Parasomnias: Unusual Behaviors During Sleep
What Are Parasomnias?
Parasomnias include sleepwalking, night terrors, and REM Sleep Behavior Disorder (RBD).
Causes of Parasomnias
- Genetics: Family history increases risk.
- Stress and Trauma: PTSD can trigger episodes.
Treatment for Parasomnias
- Safe Sleep Environment: Removing hazards.
- Managing Stress: Therapy, relaxation techniques.
- Medication: In severe cases.
Conclusion
Sleep disorders can significantly impact quality of life. If you suspect you have a sleep disorder, consult a specialist to explore effective treatment options. Don't forget to drop a comment below!
For further readings, see related articles below:

.png)









.png)

0 Comments